Understanding serverless computing: how you can use it and how to secure it
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Thursday, November 17, 2022

What is serverless computing?
Serverless computing is a collection of services provided by cloud vendors. It allows users to write and execute code in the cloud without setting up the environment and allocating resources such as VMs beforehand.
Benefits of serverless computing are:
- A pay-as-you-go model, allowing code to only run when needed,
- No server management required, since your code is running in the cloud, and you don't have to deal with the environment settings,
- Granular updates and patches that allow developers to make changes at function-level and quickly deploy new versions,
- High reliability applications, since the code runs on the cloud.
Services offered by cloud vendors
To further understand what serverless computing has to offer, we must look at services on the market and their features.
1. AWS Lambda and AWS Fargate
AWS Lambda is a compute service that allows users, through functions, to run event-driven code without server provisioning or management. AWS Lambda can be used for:
- File processing,
- Stream processing,
- Web and mobile applications,
- IoT backends, and others.
The event-driven flows help reduce costs for users and add flexibility. Lambda functions are triggered by events, and customers only pay for the time the code is running.
Moreover, when creating a Lambda function, you can either start writing a function from scratch, or use sample code such as Amazon’s blueprints or the AWS Serverless Application Repository to implement your desired code.
AWS Fargate is a compute engine that provides a serverless solution for application deployment by removing the need for infrastructure management.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a service that allows Kubernetes instances to run both in the cloud and on-premises. EKS, together with AWS Fargate, produce a serverless solution for containers.
Fargate can also be used with Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS), with no additional changes required for your applications.
2. Azure Serverless
Microsoft Azure offers a collection of serverless compute solutions. Just like AWS Lambda, Azure Serverless enables its users to deploy code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Some of the Azure compute services are:
- Serverless Functions. Just like AWS Lambda, Azure allows users to write event-driven code in their preferred language. Costs are applied only when the code is being executed,
- Serverless Kubernetes. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), together with AKS virtual nodes, provide a serverless solution that reduces the infrastructure management workload of Kubernetes clusters.
- Serverless Containerized Microservices. With this solution, applications are deployed in containers without managing the infrastructure,
- Serverless Application Environments. Using Azure App Service, web, mobile, and API applications are hosted in a fully managed environment.
Azure also provides low-code or no-code application development with Power Apps. This feature allows developers to construct applications using drag-and-drop functionalities, connectors, and readily-available solutions for common use cases.
3. Cloud Run and Cloud Functions by Google Cloud
These two solutions offered by Google Cloud provide serverless compute services.
Cloud Run is an application development tool that separates infrastructure management from the code by placing applications in containers. Using Cloud Run, microservices can be deployed without specific configurations. It is highly scalable, and it can scale to zero – this means that if a service has no requests, all containers are removed, reducing costs. It supports the following programming languages: Go, Python, Java, Node.js, Ruby, .NET, as well as others.
Cloud Functions is a similar service to AWS Lambda and Azure Serverless.
Possible vulnerabilities of serverless computing
1. Lack of source code security
Many cyber attacks are successful due to poor code security.
According to OWASP Top 10, one of the most common attacks on web applications in 2022 was SQL Injection. Whether an application is hosted in the cloud or not, user input should always be treated very carefully.
To correctly handle data received from users, you should sanitize it correctly and use prepared statements.
2. Outdated or unpatched libraries, packages, and dependencies
Another element that affects applications' security is the libraries, packages, technologies, and dependencies used.
In 2021, a critical vulnerability was discovered. Log4j, a popular Java framework used for logging messages in applications, introduced a massive flaw: it allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code on the host machine. This vulnerability, CVE-2021-44228, commonly known as Log4Shell, affected around 3 billion devices.
Serverless functions in the cloud were not immune to this attack. The functions written in Java that were using Log4j were vulnerable to Log4Shell.
While not having to deal with underlying infrastructure management is an advantage of serverless computing, technologies used by developers still have to be used safely.
How do you protect your code from such vulnerabilities?
- Only use trusted libraries,
- Apply updates and patches as they appear,
- Continuously assess your code,
- Remove any unnecessary dependencies.
3. Monitor your cloud infrastructure
This measure is a given. Log and monitor what your applications do to identify any odd behavior.
Document every event that interacts with your code and see how your applications respond.
4. Integrate cryptography into your code
Encrypt sensitive data to ensure confidentiality in your applications’ flow. You should encrypt data in transit using TLS/SSL and at rest data using AES.
Moreover, safely store secrets and keys in Hardware Security Modules (HSM) or in your cloud using services such as:
- Azure Key Vault,
- AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS),
- Cloud Key Management Service in Google Cloud.
Do not store keys, connection strings, or passwords in the source code or in plain text.
5. Too much information is disclosed in error messages.
We’ve all encountered verbose error messages.
Developers should not disclose information about errors or exceptions to the user. Instead, they should be handled in the code, and the message displayed should offer minimal explanations without revealing why the error occurred.
While writing code in the cloud and quickly deploying it without infrastructure management is tempting, you should be careful.
Implement the best practices recommended in this article to address serverless computing vulnerabilities and secure your cloud environment.
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Sabrina Lupsan merges her academic knowledge in Information Security with practical research to analyze and strengthen cloud security. At Cyscale, she leverages her Azure Security Engineer certification and her Master's in Information Security to keep the company's services at the leading edge of cybersecurity developments.
Further reading
Cloud Storage
Misconfigurations

Build and maintain a strong
Security Program from the start.
Cloud Compliance in
2023: An In-Depth Guide
The whitepaper talks about ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA.
Download WhitepaperShare this article
Stay Connected
Receive our latest blog posts and product updates.
TOP ARTICLES
Cloud Security
Our Compliance toolbox
Check out our compliance platform for cloud-native and cloud-first organizations:
LATEST ARTICLES
What we’re up to
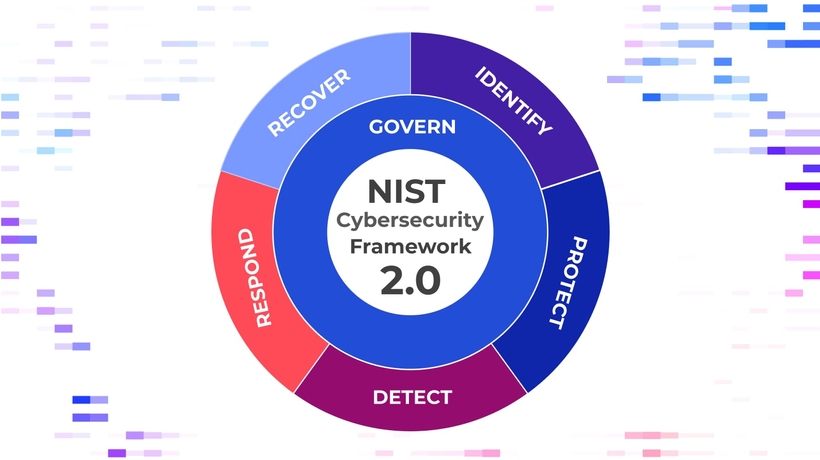
NIST CSF 2.0: A Detailed Roadmap for Modern Cybersecurity



