What Is Data Classification And Why Is It Important?
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Thursday, July 21, 2022

What is data classification?
Data classification is a way of grouping data to ensure easy sorting, retrieval, and prioritization.
The data is divided into categories, and a label, or a tag, is applied to make it easily searchable.
The three commonly used types of data classification are:
- Content-based, which is done solely based on the information involved,
- Context-based, which takes into account the location of the data, the owner, the application it is used in, and others,
- User-based, which requires users to label data based on internal rules.
In this article, we will understand how valuable data classification is for a company using cloud services, as well as how AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud handle the process of labeling/tagging assets.
Benefits of data classification
1. Risk management
According to AWS, data classification is a foundational step in cybersecurity risk management. The reason behind this is that applying labels to data and establishing security requirements such as:
- the level of confidentiality,
- the need for integrity checking,
- the sensitivity of data,
can help your company manage risks efficiently.
2. Compliance
When implementing compliance with international standards, you must know what type of data your company is managing and storing.
Data classification should be done correctly to understand which of the data you're storing is confidential/sensitive. You cannot comply with recognized frameworks unless you correctly handle confidential data (and you cannot do this unless you know which data is confidential).
Let’s look at a scenario – if you’re storing customer PII, but you are not aware of the criticality of that data, you may not even think of protecting it, for example, by encrypting it.
Therefore, your company may not be compliant with standards like:
- SOC 2,
- PCI-DSS,
- GDPR, and others.�
3. Security
Organizing data into categories and using labels can help you maintain:
- confidentiality, because you will turn your focus to the most sensitive data,
- integrity, because you can mark the need for integrity as high for some data using labels,
- availability, which can be explicitly ensured for data that needs to be highly available and is labeled as such.
Much of the data that used to be saved on-premises is now saved and processed in the cloud, in databases, assets of type storage, and others.
Therefore, data classification should be used in the cloud. Let’s look at what the cloud industry offers to help you easily and accurately classify your data.
Data classification – an industry overview
We will look at the top 3 cloud vendors – AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud – to see how data classification is implemented and the different types of tags that can be applied depending on the cloud service selected.
1. Amazon Web Services
In the AWS documentation, a three-tiered classification is recommended, with the following tag names:
- Unclassified,
- Official,
- Secret and above.
Moreover, AWS presents the following three labels used by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), a United States government agency, and recommends them:
- Low,
- Moderate,
- High,
which classify the impact a potential data breach would cause on that data.
However, these tags are recommendations and users can implement their own tags. Later in this article, you will find best practices on how to implement labeling for your cloud environment.
When you create a resource in AWS, you can add tags (key-value pairs) to the resource to associate it to labels used in data classification.
2. Google Cloud Platform
For data classification in Google Cloud, we can find both labels and tags, which are two different things.
A label is described as a key-value pair that you can create using the Resource Manager API and the Google Cloud console. These can be used to separate resources in terms of billing, to add information about resource state, and so on.
Tags, however, are the tools that allow Google Cloud customers to classify data and establish rules based on their classification.
The difference between labels and tags in Google Cloud is that labels are simply metadata added to resources, while tags categorize assets and can be used when defining policies and rules (for example, who is allowed to access a certain asset) in your Google Cloud environment.
3. Microsoft Azure
In Microsoft Azure, we can use the Microsoft Purview service to ensure data labeling of cloud assets.
Microsoft Purview is a solution offered by Microsoft that brings together your cloud, on-premises, and SaaS data and helps you manage it through different solutions:
- Data Map,
- Data Catalog,
- Data Sharing,
- Data Estate Insights, and others.
An important aspect is that Data Map powers most of the solutions offered by Microsoft Purview and is a paid service.
In terms of data classification, there are a few services that can help you manage your cloud resources:
- the Microsoft Purview Data Catalog uses sensitivity labels that can be added to cloud assets.
- the Microsoft Purview Information Protection service, which has the following features: data classification, trainable classifiers, sensitive information types,
- the Azure Information Protection unified labeling client, a downloadable client that also provides sensitivity labels.
Microsoft Azure suggests that you apply tags that contain additional information about resources (do not include any PII or sensitive data in the tags) to:
- add context to your resources and understand them better,
- be able to use complex filters.
Azure also suggests a “Data classification” tag to describe the sensitivity of data stored or processed by a resource. If an organization does not have their own labels defined, they may use the following values supplied by Microsoft:
- Non-business,
- Public,
- General,
- Confidential,
- Highly confidential.
Moreover, Azure recommends that you also use a formal data classification process. In the next section, we will explain best practices to keep in mind when classifying your resources.
How do you implement data classification?
An important rule to follow when implementing data classification is that the entire organization should use the same classification tags/labels. Using a policy or a procedure for this process that regulates:
- the classification process as a whole,
- the tags’ names, and others
is essential to ensuring consistent data classification.
In Cyscale, you can find the out-of-the-box “Data Management” policy, which contains the “Data Classification” procedure to guide you in this process. Moreover, you can create your own custom policy with any specific rules you want to add.
Considering the benefits of data classification, implement this feature for your cloud environment. Use a company-level classification policy and add tags to your cloud assets to enable easy sorting, retrieval, and prioritization.
In Cyscale, you can use this feature to:
- easily filter assets based on tags,
- highlight any irregularities regarding your most sensitive assets, and
- prioritize remediation for the most urgent findings.
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Sabrina Lupsan merges her academic knowledge in Information Security with practical research to analyze and strengthen cloud security. At Cyscale, she leverages her Azure Security Engineer certification and her Master's in Information Security to keep the company's services at the leading edge of cybersecurity developments.
Further reading
Cloud Storage
Misconfigurations

Build and maintain a strong
Security Program from the start.
Cloud Compliance in
2026: An In-Depth Guide
The whitepaper talks about ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA.
Download WhitepaperShare this article
Stay Connected
Receive our latest blog posts and product updates.
TOP ARTICLES
Cloud Security
Our Compliance toolbox
Check out our compliance platform for cloud-native and cloud-first organizations:
LATEST ARTICLES
What we’re up to
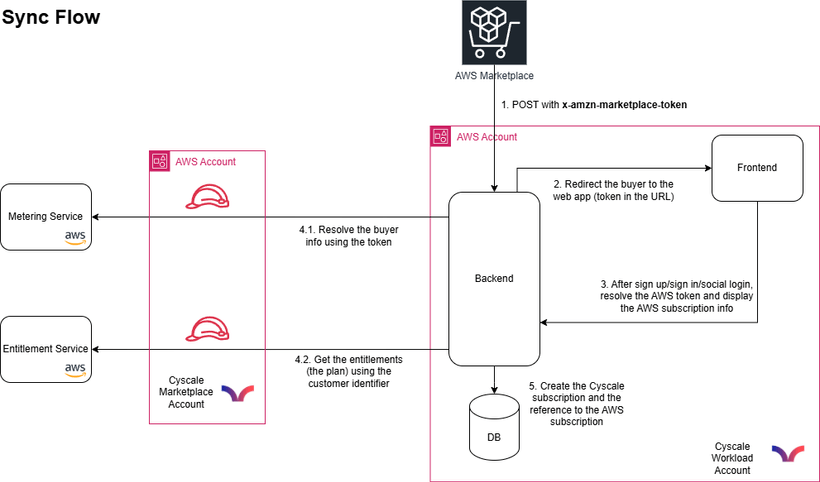
Cyscale on AWS Marketplace Simplifies CNAPP Procurement and Deployment