CONTENTS
Everything You Need to Know about HITRUST Compliance in the Cloud
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Tuesday, November 7, 2023

As well as delivering innovation and improving care for customers, organizations operating in the healthcare industry are also required to demonstrate robust processes in security, data protection and privacy, and HITRUST is considered by many the best-in-class for data security and privacy healthcare certification.
HITRUST (Health Information Trust) Alliance is the organization that established the HITRUST CSF (Common Security Framework), a framework for managing and securing information in the healthcare industry. This comprehensive framework regulates how healthcare providers and other health businesses handle sensitive data, store it and protect it.
The HITRUST framework goes above and beyond what HIPAA requires and while its stringency can make it daunting to implement, the benefits of this certification in terms of credibility and assurance are not to be underestimated.
HITRUST CSF is based on ISO/IEC 27001 and 27002 and incorporates more than 50 regulations, standards, and frameworks, thus providing a complete set of requirements and best practices to ensure security.
In this article, we will look at the requirements that apply specifically to healthtech companies with apps and data in the cloud and how to ensure your security and compliance processes are robust enough to pass HITRUST certification.
HITRUST control categories and how they relate to cloud security
The standard contains 14 control categories, numbered from 0 to 13:
- Information Security Management Program
- Access control
- Human Resources Security
- Risk Management
- Security Policy
- Organization of Information Security
- Compliance
- Asset Management
- Physical and Environmental Security
- Communications and Operations Management
- Information Systems, Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance
- Information Security Incident Management
- Business Continuity Management
- Privacy Practices
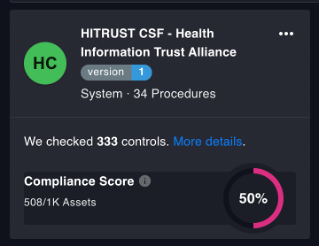
Each control category has one or more objectives, which define the purpose or scope of its requirements, and each Objective contains control references, which encompass a best practice or requirement. There are 49 objectives and 156 control references.
This standard can become overwhelming, especially when looking at the 516 pages of version 11.2.0 (the latest one as of November 2023), making implementation a daunting task for small or inexperienced teams. But as we said, the benefits in terms of credibility and increased confidence from your customers cannot be underplayed. Furthermore, there are solutions out there that can do the heavy lifting, such as ensuring your cloud security controls are in compliance with the framework and alerting you if drifts are detected.
Access control for the cloud under HITRUST CSF
The "Access control" category includes recommendations on user management, password policies, the Least Privilege principle, network segregation, session timeout, teleworking, and many others—everything related to authentication and authorization.
Effective cloud user password management
Implementing a robust password policy is very important. Imposing a minimum number of characters, as well as the usage of special characters, lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and other conditions, is imperative because users tend to want to choose passwords that are easy to remember and type, which increases the risk of having credentials stolen through brute force. Moreover, users should be prohibited from using the same password twice and having old passwords in use.
How do you implement an effective password policy in the cloud?
To ensure users implement secure passwords, use the following checklist:
- a minimum length of 14 characters,
- no password reuse for 24 months,
- at least a lowercase character,
- at least an uppercase character,
- at least a digit,
- at least one symbol.
Although this seems like a lot to consider, it only takes a few minutes to make a great password policy, and for AWS, for example, you can do this in one quick command:
aws iam update-account-password-policy --minimum-password-length 14 --password-reuse-prevention 24 --require-lowercase-characters --require-uppercase-characters --require-numbers --require-symbols
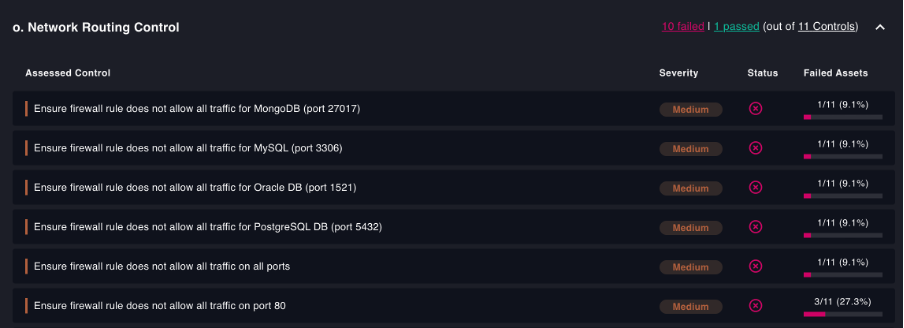
Network Routing Control for cloud infrastructure
Routing controls should be in place to prevent unnecessary connections and information flows across your cloud infrastucture, according to HITRUST CSF.
Firewalls can block unwanted traffic to your cloud, and we recommend filtering traffic by allowlisting IP addresses and ports to reduce the attack surface and further control the access. CSPM tools such as Cyscale provide a wide range of security controls that granularly verify that firewall rules are written for the most important ports, such as databases.
Securing Human Resources in the cloud
The next category is “Human resources” and focuses on security and compliance processes that apply during the entire lifecycle of an employee in a company, starting from “Prior to Employment”, through “During On-Boarding”, “During Employment”, all the way up to “Termination or Change of Employment”. Appropriate application of policies and procedures should ensure that every employee is set up with relevant levels of entitlement and privilege to cloud systems and infrastructure, and that those entitlements and access are revoked when the employee leaves.
Poor access management processes can result in overprivileged users that unnecessarily expand your attack surface.
Cloud Roles and Responsibilities
Under “Prior to Employment”, the first requirement is “Roles and Responsibilities”.
There should be a clear definition of roles according to the existing information security policy. This umbrella covers the protection of data by allowing only authorized access. We have a complete guide on best practices for IAM in the cloud.
We’ve put our recommendations into a checklist:
- enable MFA for all users,
- grant users access to resources, services, and data at group level. You can either directly assign the user permissions or add the user to a group and assign permissions at group level. The second one is recommended because you simplify access management.
- comply with the Least Privilege principle to only assign the necessary permissions for the required amount of time, and others.
Compliance controls for cloud assets
Jumping to the sixth control category, “Compliance”, there are several technical requirements relevant to cloud infrastructure in the healthcare sector.
Data Protection in the cloud and Privacy of Covered Information
To ensure the confidentiality of data, encryption should be enabled for cloud assets that contain sensitive information. This section of the HITRUST standard refers to how encryption should be applied. Here is a comprehensive guide on data encryption in all its states - data in use, data in motion, and data at rest.
Regulation of Cryptographic Controls
Encrypting data is only effective if the used cryptographic algorithms are industry-recommended. For example, if a vulnerable version of SSL/TLS is deployed, data in transit is unprotected. TLS 1.2 is recommended for securely transporting data.
For encryption of data at rest, AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard with a key of 256 bits) is the standard.
Protecting your cloud environment and your code
The 9th control category, “Communications and Operations Management" in HITRUST CSF covers segregation of duties, change management, malicious code, back-ups, and many other controls. These are most relevant to cloud security:
Effective change management in the cloud
To ensure comprehensive change management in the cloud, log and monitor all users' actions. This helps you identify and control changes that occur in the cloud environment. To configure a comprehensive change management process, consider logging changes to:
- firewall rules,
- IAM policies,
- routing tables,
- network gateways,
- VPCs,
- SQL instances, and others.
Controls against malicious code in the cloud
There are a number of things you can do to protect your cloud apps and data against malware. Scan your VMs for malicious programs and make sure their configurations are secure. In Google Cloud, you can deploy your VMs in a hardened state by enabling the “Shielded VM" option to prevent malicious code, such as rootkits and backdoors, from infiltrating your cloud environment.
Turning on Shielded VM in Google Cloud takes just a few clicks. Navigate to the VMs' "Security" configurations and tick all boxes under this feature.

Cloud back-ups best practices
The “Back-up” category not only recommends performing regular back-ups, but also having recovery procedures in place for highly sensitive cloud resources, such as key vaults.
Make cloud data back-ups and store them separately from the original cloud environment; you can store them in different data centers and regions and use availability zones to ensure that if an unforeseen event occurs at one datacenter, you can still restore a back-up with little to no delay.
Moreover, enable soft delete for resources that allow this to make sure you’re not deleting a cloud asset that you didn’t mean to delete. For example, Azure Key Vault has soft delete, as well as purge protection. Soft delete allows you to restore the key vault after deletion for a period set by you (between 7 and 90 days), while purge protection will not allow you to purge the key vault (delete forever) manually. You can enable both of these settings quickly with the following command:
az resource update --id <resourceID> --set properties.enablePurgeProtection=true properties.enableSoftDelete=true
Audit Logging, Monitoring System Use, Protection of Log Information, Administrator and Operator Logs in the cloud
There are so many control references for logging it can get a bit overwhelming, so let’s break this section apart to make it more manageable.
Audit Logging and Monitoring System Use are quite similar. The first requires you to log user activity and security events, while the latter refers to information processing systems.
Protection of Log Information recommends that logs are protected from tampering or unauthorized access. Consider securing the bucket or storage account where logs are collected; it is easy for companies to forget to secure logging storage assets because they’re more focused on the sensitive data, especially in regulated sectors like healthcare.
Administrator and Operator Logs require that high-privilege actions should be logged. For example, the usage of the “root” account in AWS should be logged in order to keep track of who accesses it and why.
Automating cloud security and HITRUST compliance
HITRUST CSF is a very complex and detailed compliance standard that can be overwhelming to understand and daunting to implement. What we have covered in this article may only scratch the surface but should serve as a solid foundation on your journey to bringing your cloud compliance in alignment with the framework.
To make the overall process more manageable, consider a solution such as the Cyscale cloud securty platform to keep track of your progress, monitor for drifts, and automate security checks that validate your efforts toward achieving HITRUST compliance. Cyscale has over 300 controls that verify your cloud settings against the HITRUST CSF standard and features easily exportable reports to better illustrate your efforts to an auditor, speeding your journey to accreditation.
Further reading
Cloud Compliance in
2025: An In-Depth Guide

The whitepaper talks about ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA.
Download WhitepaperCloud Storage
Misconfigurations
Build and maintain a strong
Security Program from the start.
Share this article
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Sabrina Lupsan merges her academic knowledge in Information Security with practical research to analyze and strengthen cloud security. At Cyscale, she leverages her Azure Security Engineer certification and her Master's in Information Security to keep the company's services at the leading edge of cybersecurity developments.
Stay Connected
Receive our latest blog posts and product updates.
TOP ARTICLES
Compliance
Our Compliance toolbox
Check out our compliance platform for cloud-native and cloud-first organizations:
LATEST ARTICLES
What we’re up to
Why the world needs Cyscale in a post-Wiz era