NIST Compliance in the Cloud
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Wednesday, January 11, 2023

The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a non-regulatory US government agency that develops best practices and security standards for government organizations or contractors.
NIST compliance is mandatory for government contractors handling government data. Still, companies outside this range also choose to become NIST compliant due to the excellent reputation and benefits of the standard.
Three NIST frameworks can be used when establishing NIST compliance:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework,
- NIST 800-53,
- NIST 800-171.
Let’s look at them in detail to understand the differences.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) gathers best practices and standards to help companies build a robust cybersecurity program and manage risk.
The framework contains 5 core functions, which contain 23 categories, which in turn are divided into 108 subcategories formulated as outcomes. Organizations can formulate their own controls or use the suggested ones corresponding to NIST SP 800-53.
The core functions are:
- Identify,
- Protect,
- Detect,
- Respond,
- Recovery.
The Identify function focuses on the company’s efforts to assess and understand:
- Risk,
- The business environment,
- Assets,
- The supply chain, and others.
Identify is the first step to securing your cloud environment; having a good grasp of your assets and their relations can provide you the visibility you need to secure them and fix misconfigurations properly.
The Protect function introduces requirements regarding:
- identity management,
- access control,
- data security, and others.
We can translate to the cloud this function’s scope through the following examples:
- Assets encryption,
- Strong IAM policies,
- Compliance with the Least Privilege Principle, and others.
The third function in the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Detect, refers to the logging and monitoring of processes and events. Suspicious behavior and anomalies can be identified through careful examination of logs.
The Respond function involves incident management and incident response and ensures that the impact of a cybersecurity incident is minimized.
The last step to ensuring NIST CSF compliance is Recovery. Availability is crucial, and incidents that keep systems down can be catastrophic. To fulfill this function in the cloud, one of the solutions is to replicate and back up data in different data centers and regions to safeguard data and maintain high availability in the case of incidents.
NIST 800-53
The NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-53 is a comprehensive framework designed for governmental agencies that implement information security systems, except for those related to national security, where they can be used to complement the national security systems guidelines.
SP 800-53 has over 1000 security controls, categorized into the following 20 control families:
- Access control,
- Awareness and training,
- Audit and accountability,
- Assessment, authorization, and monitoring,
- Configuration management,
- Contingency planning,
- Identification and authentication,
- Incident response,
- Maintenance,
- Media protection,
- Physical and environmental protection,
- Planning,
- Program management,
- Personnel security,
- PII processing and transparency,
- Risk assessment,
- System and services acquisition,
- System and communications protection,
- System and information integrity,
- Supply chain risk management.
For this framework, the following steps are recommended:
- Analyze. This stage involves understanding what data the company stores and the risk associated with it, as well as possible threats.
- Tailor controls. This process involves inspecting all of the controls and establishing how each of them applies to your company, as well as adjusting them to fit your company's needs.
- Assess. A continuous analysis of the efficacy is an essential process.
For example, the first control family described in NIST SP 800-53, “Access control”, can be comprised of several cloud-specific requirements, such as:
- Assigning permissions in the cloud at group level with well-defined rules,
- Using role-based access control (RBAC) and complying with the Least Privilege Principle,
- Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users, and others.
NIST 800-171
The NIST SP 800-171 is a framework designed for non-federal companies that work with federal agencies. This framework is intended to protect controlled unclassified information (CUI).
CUI is information related to the government that is unclassified, but sensitive. For example, PII and PHI may fall under this category.
This framework contains 14 out of the 20 categories listed for NIST 800-53 and is less complex than SP 800-53. Many of the 110 controls are best practices and are easier to understand, compared to the 1000 controls existent in NIST SP 800-53.
Here’s how we can help
Choosing the right NIST framework and ensuring cloud compliance is a pivotal task.
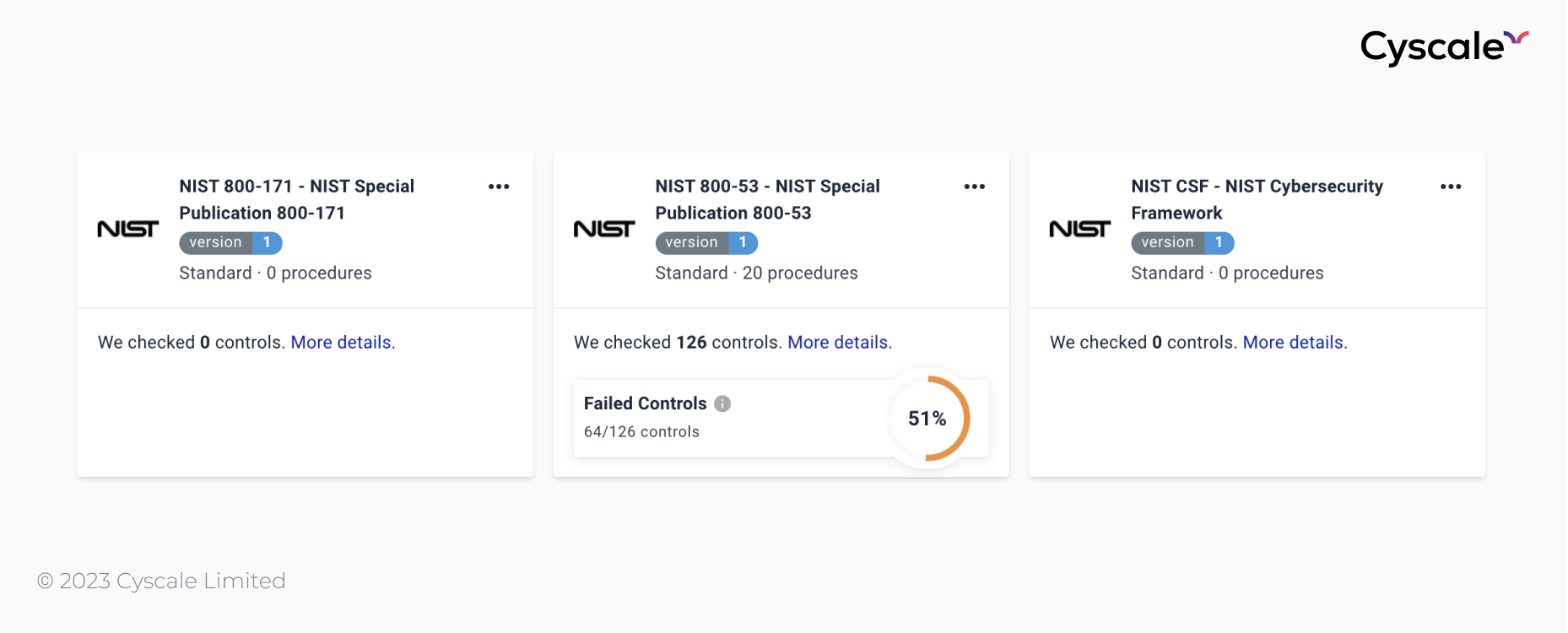
Cyscale is here to guide you, making the NIST cloud security journey simpler. Leveraging our Standards page, you can efficiently monitor your progress and expedite the compliance process, tailored for your cloud-specific requirements.
Cloud Security Analyst at Cyscale
Sabrina Lupsan merges her academic knowledge in Information Security with practical research to analyze and strengthen cloud security. At Cyscale, she leverages her Azure Security Engineer certification and her Master's in Information Security to keep the company's services at the leading edge of cybersecurity developments.
Further reading
Cloud Compliance in
2025: An In-Depth Guide

The whitepaper talks about ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA.
Download WhitepaperCloud Storage
Misconfigurations
Build and maintain a strong
Security Program from the start.
Share this article
Stay Connected
Receive our latest blog posts and product updates.
TOP ARTICLES
Compliance
Our Compliance toolbox
Check out our compliance platform for cloud-native and cloud-first organizations:
LATEST ARTICLES
What we’re up to
Why the world needs Cyscale in a post-Wiz era